Numerical 2D study of air flow controlled by passive technique in solar air collectors
Main Article Content
Abstract
The article presents a numerical simulation on air flow and heat transfer characteristics in solar air collectors mounted with obstacles. Computational Fluid Dynamics, ‘CFD’ based on the finite volume method, SIMPLE algorithm and the turbulence standard 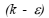 model have been implemented. A numerical 2D model of dynamic air vein solar collectors with 1400 mm length and 25 mm air gap was used to evaluate hydrodynamic and heat transfer phenomena of flow patterns in the annular passageways, precisely the heat transfer around 13 chicanes. The chicane is formed with two parts: the first is perpendicular to the air flow and the second is titled
model have been implemented. A numerical 2D model of dynamic air vein solar collectors with 1400 mm length and 25 mm air gap was used to evaluate hydrodynamic and heat transfer phenomena of flow patterns in the annular passageways, precisely the heat transfer around 13 chicanes. The chicane is formed with two parts: the first is perpendicular to the air flow and the second is titled 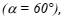 they are mounted in successive rows, oriented perpendicular to the air flow. It is apparent that the turbulence created by the chicanes resulting in greater increase in heat transfer over the air vein. The pressure drops are analyzed vs. the Reynolds number and shown good agreements with experimental and semi-empirical relationship results. The mass flow rates effect on the velocity magnitude is analyzed. It was found that the mass flow rate variation has a slight effect on velocity evolution.
they are mounted in successive rows, oriented perpendicular to the air flow. It is apparent that the turbulence created by the chicanes resulting in greater increase in heat transfer over the air vein. The pressure drops are analyzed vs. the Reynolds number and shown good agreements with experimental and semi-empirical relationship results. The mass flow rates effect on the velocity magnitude is analyzed. It was found that the mass flow rate variation has a slight effect on velocity evolution.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
-
Attribution — You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
-
ShareAlike — If you remix, transform, or build upon the material, you must distribute your contributions under the same license as the original.
- No additional restrictions — You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits.




