Influence of annealing time on structural and electrical properties of Sb doped SnO2 films
Main Article Content
Abstract
Nanocrystalline 14 at % Sb-doped SnO2 films have been synthesized by a sol-gel method, to use them as solar cells electrodes. In this paper, we present a study of the annealing time of the films versus the increase of the particle size (varying from 6 nm to 19 nm) established by Scherer’s equation. We have also followed electrical resistance evolution with annealing temperature and time. An optimum value of 222 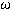 ; was measured on a sample annealed at 500 °C for 2 h. The crystalline structure of the films was characterized and phases identified by X ray diffraction in grazing incidence. Their thickness has been measured by spectroscopic ellipsometry around 200 nm.
; was measured on a sample annealed at 500 °C for 2 h. The crystalline structure of the films was characterized and phases identified by X ray diffraction in grazing incidence. Their thickness has been measured by spectroscopic ellipsometry around 200 nm.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
-
Attribution — You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
-
ShareAlike — If you remix, transform, or build upon the material, you must distribute your contributions under the same license as the original.
- No additional restrictions — You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits.




