Growth by the Heat Exchanger Method and Characterization of Multi-crystalline Silicon ingots for PV
Main Article Content
Abstract
Multi-crystalline silicon ingots of 44 cm square cross section, weighing 80 kg, have been produced by a modified Heat Exchanger Method in which a graphite insulation and heat exchanger block move down from the heater during crystal growth to facilitate heat extraction from the bottom of the crucible. Wafers of 300 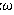 thickness and 1.2
thickness and 1.2 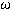 resistivity, have shown consistency and uniformity in the properties required for large-scale production. The interstitial oxygen concentration varies from 1.6 to 3.6 ppm, whereas the substitutional carbon concentration is assessed to be below 10 ppm.
resistivity, have shown consistency and uniformity in the properties required for large-scale production. The interstitial oxygen concentration varies from 1.6 to 3.6 ppm, whereas the substitutional carbon concentration is assessed to be below 10 ppm.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
-
Attribution — You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
-
ShareAlike — If you remix, transform, or build upon the material, you must distribute your contributions under the same license as the original.
- No additional restrictions — You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits.




